
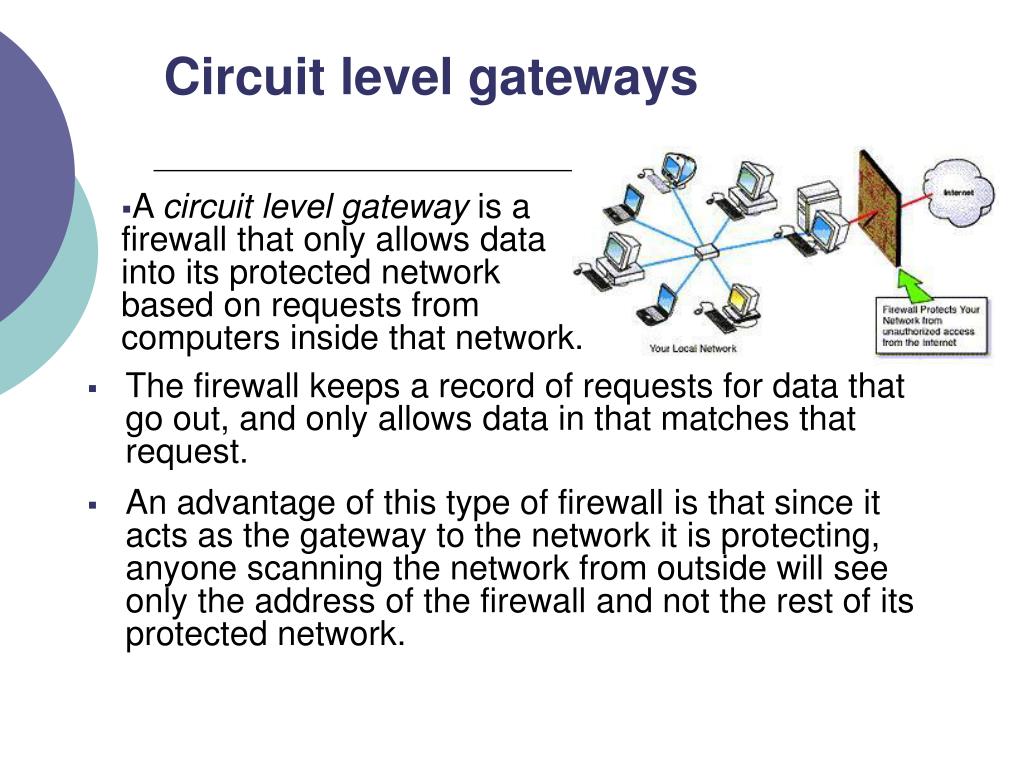
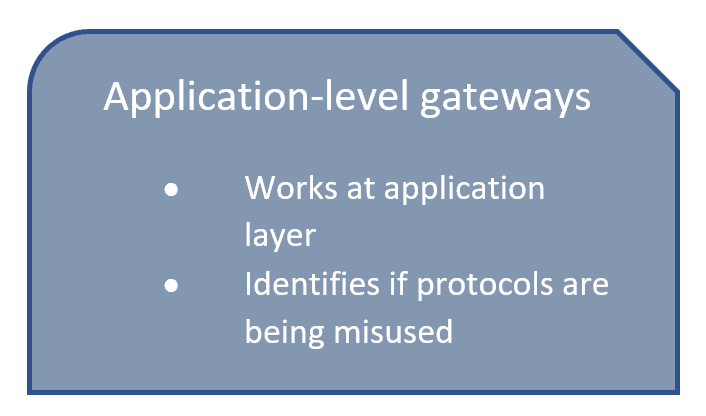
Protocols that do not carry the source and destination IP addresses include HTTP, TFTP, telnet, archie, finger, Network Time Protocol (NTP), Network File System (NFS), remote login (rlogin), remote shell (rsh) protocol, and remote copy (rcp). NAT performs translation services on any TCP/UDP traffic that does not carry source and destination IP addresses in the application data stream. This module also provides information about the protocols that use ALGs for IP header translation. This module describes the basic tasks to configure an application-level gateway (ALG) with Network Address Translation (NAT).
Example: Enabling MultiPart SDP Support for NAT.Example: Enabling SPI Matching on Endpoints.Example: Disabling SPI Matching on the NAT Device or Changing the Default Port.Example: Configuring IPsec ESP Through NAT.Configuration Examples for Using Application-Level Gateways with NAT.Disabling SPI Matching on the NAT Device or Changing the Default Port.
How to Configure Application-Level Gateways with NAT.NAT Support of Skinny Client Control Protocol.NAT Support for SIP-Voice and Multimedia over IP Networks.NAT Segmentation with Layer 4 Forwarding.NAT Support for H.323 v3 and v4 in v2 Compatibility Mode.NAT Support for Application-Level Gateways.
Information About Using Application-Level Gateways with NAT.Restrictions for Using Application-Level Gateways with NAT.Prerequisites for Using Application-Level Gateways with NAT.Using Application-Level Gateways with NAT.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
